

As the basis for making photovoltaic cells and integrated circuits, silicon wafer cleaning is very important. The effect of cleaning directly affects the final performance, efficiency and stability of photovoltaic cells and integrated circuits. Cleaning the silicon wafer not only removes impurities on the [...]
Antireflection-Coated Blue GaN Laser Diodes in an External Cavity and Doppler-Free Indium Absorption Spectroscopy Commercially available GaN-based laser diodes were antireflection coated in our laboratory and operated in an external cavity in a Littrow configuration. A total tuning range of typically 4 nm and an [...]
PAM XIAMEN offers Ce:YAG substrate. Ce:YAG substrate (111) 5 x 5 x 0.5 mm, 2sp Substrate Specifications Crystal: Ce: YAG ( 0.2% wt Ce doped) Size: 5 x 5 x 0.5mm +/-0.05mm Orientation: (111) +/-0.5 0 Polish: two sides optical polished. Pack: Packed in 1000 class plastic [...]
PAM XIAMEN offers high-quality Al2O3 (Sapphire). R-Plane (1-102) Square Al2O3(11-02) substrate Al2O3- Sapphire Wafe, R Plane, 5x5x0.5mm, 1SP Al2O3-Sapphire Wafe, R Plane, 5x5x0.5mm, 2SP Al2O3- Sapphire Wafer, R Plane, 10x10x0.5mm, 1SP Al2O3-Sapphire Wafer, R Plane, 10x10x0.5mm, 2SP Al2O3- Sapphire Wafer, R Plane, 10x10x1.0mm, 1SP Al2O3-Sapphire Wafe, R Plane, 0.5″x0.5″x0.5 [...]
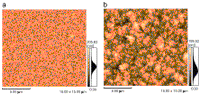
Silicon wafers contribute significantly to the photovoltaic module cost. Kerfless silicon wafers that grow epitaxially on porous silicon (PSI) and are subsequently detached from the growth substrate are a promising lower cost drop-in replacement for standard Czochralski (Cz) wafers. However, a wide technological processing [...]
The Japanese component manufacturing company Namiki recently announced several technological advancements and equipment upgrade for advanced industrial component production. Namiki successfully produced unprecedented large sized diamond substrates and realized the bonding of two different materials under room temperatures; moreover, the corporation reinvented its cleaning [...]
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
