Total Thickness Variation (TTV): The maximum variation in the wafer thickness. Total Thickness Variation is generally determined by measuring the wafer in 5 locations of a cross pattern (not too close to the wafer edge) and calculating the maximum measured difference in thickness. The TTV (Total Thickness Variation) value is used to determine the surface quality parameters of the thinned wafer, which will directly affects the subsequent packaging process and the final quality of the chip. Generally, the smaller the TTV, the better the intra-chip uniformity. The wafer TTV from PAM-XIAMEN can meet your process requirements.
1. Why Does the Total Thickness of a Wafer Vary?
The total thickness of a wafer can vary for a number of factors during the grinding process, specifically shown as Table 1:
|
Table 1 Factors affecting TTV |
|
| No. | Factors |
| 1. | The angle between the grinding wheel spindle and the support table does not meet the technological requirements |
| 2 | Flatness of the table surface |
| 3 | The axes of the support tables are not parallel |
| 4 | The cleanliness of the support table and whether there is any residue |
| 5 | Wheel quality |
| 6 | Grinding process parameters |
| 7 | Grinding feed system stiffness |
| 8 | System stiffness of support table |
Among all the factors, the fundamental factor is that the angle between the spindle and the support table meets the process requirements. There is a certain angle between the grinding wheel and the support table, which is the key process to obtain better wafer thinning surface quality, control TTV, prolong the life of the grinding wheel and reduce the internal stress of thinning.
2. How to Control TTV to Meet User Process Requirements?
As shown in Figure 1, the guarantee of the angle value △β between the grinding wheel main shaft and the support table is mainly realized by adjusting the angle of the main shaft or the bearing table. Through adjustment, the △β angle between the main shaft and the bearing table can meet the process requirements.
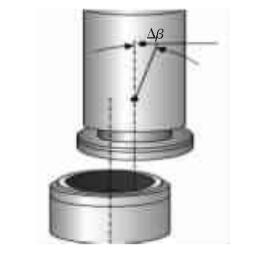
Fig. 1 Angle between Main shaft and Support Table
In the end, the grinding wheel grinding state as shown in Figure 2 will be achieved, that is, during the grinding wheel grinding process, only the 0B section of the grinding wheel is the main grinding area, which is also the key area to ensure the TTV in the wafer. Before cutting, the angles of the axis relative to the three points of B0A of the wafer are 0, 0, and -20° respectively. The key point that affects TTV is to ensure that the relative angle between point 0 and point B is 0.

Fig. 2 Grinding
The key to solving this problem is to adjust the deviation online according to the wafer grinding accuracy. Its adjustment principle is that after the initial manual adjustment of the equipment is completed, the wafer is ground and scanned by a non-contact online measuring device to obtain the TTV value of the wafer and the specific position of the wafer thickness. According to the specific thickness parameters, the correlation function is calculated, and the angle is adjusted through the automatic control device.
This adjustment process is: grinding according to the manually adjusted wafer, measuring the TTV value of the first wafer online, adjusting the angle according to the measurement result, and then grinding the wafer. The value will be gradually reduced until the user process requirements are met.
For more information, please contact us email at victorchan@powerwaywafer.com and powerwaymaterial@gmail.com.

