Differential magnetoresistive sensor for sale from PAM-XIAMEN is one of magnetoresistive sensors, which is packaged by indium antimonide (InSb) thin film magnetoresistor plus bias magnet with a metal shell. As a result, the output signal is a quasi-sine wave signal. The specification of differential magnetoresistive (MR) sensor provided is as following:
Differential Magnetoresistive Sensor Image
1. Differential Magnetoresistive Sensor Datasheet
This differential magnetic resistance sensor has a low resistance from 300 ohm to 900 ohm with a size of Dia. 10mm.
| Technical Parameters | PAM10-10L | PAM10-10D |
| Maximum Working Voltage | DC 10V | DC 10V |
| Rated Working Voltage | DC 5V | DC 5V |
| Output Offset Voltage, at Vin
25℃δ=∞ |
≤130 mV | ≤130 mV |
| Output Amplitude , 25℃δ=0.15mm,
Standard Target Object |
>900 mV | >1000 mV |
| Total Resistance R1-3,25℃,
I<1mA, δ=∞ |
220-900Ω | 900-1600Ω |
| Resistance Asymmetry(R12 & R13)25℃,δ=∞
|
≤10% | ≤10% |
| Cut-Off Frequency | >20KHz | >20KHz |
| Working Temperature
|
-30~70℃ | -30~70℃ |
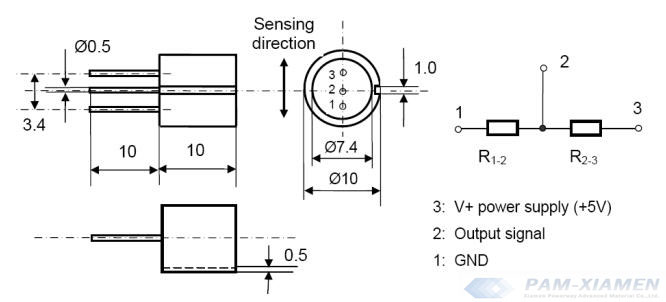
Differential MR Sensor Dimensions:
2. What Is a Magnetoresistive Sensor ?
Magnetoresistive effect sensor is made based on the magnetoresistance effect of magnetic materials. Magnetic materials have anisotropy characteristic. When magnetizing it, the direction of magnetization will depend on the material easy axis, the shape, and the magnetizing magnetic field direction. When a current I is applied to the strip-shaped permalloy material, the resistance of the material depends on the angle between the direction of the current and the direction of magnetization.
If a magnetic field B (the measured magnetic field) is applied to the material, the original magnetization direction will be rotated. If the magnetization direction turns to the direction perpendicular to the current, the resistance of the material will decrease; if the magnetization direction turns to the direction parallel to the current, the resistance of the material will increase. Magnetoresistive based sensors generally consist of four such resistors and connect them to form a bridge. Under the action of the measured magnetic field B, the resistance values of the two resistors located at opposite positions in the bridge increase, and the resistance values of the other two resistors decrease.
3. What Are Magnetoresistive Sensor Types ?
Magnetoresistive sensors can basically be divided into two categories:
Firstly, in the application of high magnetic field, when the applied field intensity is high enough to saturate the soft magnetic sensor material, the magnetic vector in the sensor is almost parallel to the applied field. Therefore, non-contact magnetoresistive angle sensor is a common application of magnetoresistive high-field sensor.
Secondly, as for the low magnetic field application, the form of the strip determines the magnetization vector, because a natural preference for longitudinal rheology is shown by the magnetization. The external magnetic will cause a magnetization distortion in the strip, changing the resistance due to the MR effect. Thereby, linear low magnetic field sensor is usually used in this pattern.
Magnetoresistive Sensor V.S. Hall Effect Sensor
The sensitivity and linearity of magnetoresistance sensor have been able to meet the requirements of magnetic compasses, and its performance in all aspects is significantly better than Hall devices. Hysteresis error and zero-point temperature drift can also be eliminated by alternating forward and reverse magnetization of the MR sensor. Because of these superior performance of magnetoresistive sensor, it can compete with fluxgate in some applications.
4. How Does a Differential Magnetoresistive Sensor Work ?
Imposing bias magnetic fields or magnetic iron in the back of the film magnetic reluctance is the core structure of differential magnetoresistive sensor. The magnetic field in the MR 1 and MR 2 will increase one by one, leading to a increase in the resistance of MR 1 and MR 2 when the ferromagnetic objects or magnet through the detecting area. Apply a voltage of Vcc at the end of ① and ③, there will be a sine wave at ② end. Please see the Fig. in the following:

5. Differential Magnetoresistive Sensors Properties
There are many characteristics of differential magneto resistive sensor:
- It can sense a wide range of speed;
- It has a rugged metal housing;
- The signal amplitude has nothing to do with speed;
- There is a built-in bias magnet;
- It is best for harsh environments.
6. Differential Magnetoresistive Sensor Applications
Due to the excellent properties of differential magnetic resistance sensor, it can be used in various applications, like detecting speed, detecting angle, detecting RPM of electric spindle, measuring RPM of PCB punch, measuring linear small displacement and etc. Specifically:
6.1 Measuring RPM of PCB by Differential Magneto Resistive Sensor
The sensor of differential magnetic resistance is widely applied in the measuring the speed of ferromagnetic rotors, like slotted disk, gears, and rack. A stable sine wave can be got after installing correctly.
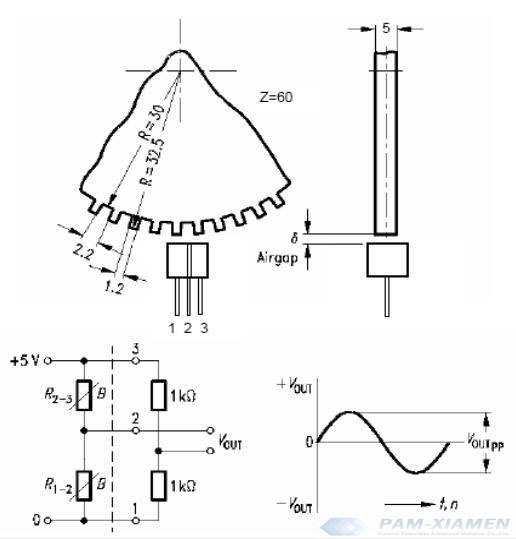
The usage of differential MR sensor in controlling excavator angle displacement :

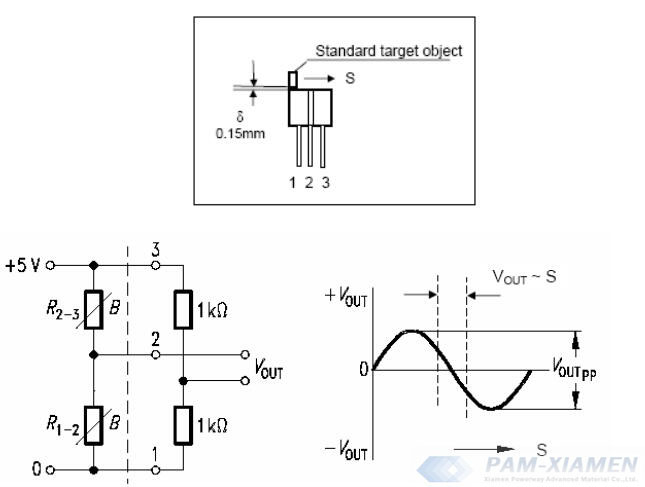
6.2 Differential MR Sensor Measuring Small Displacement
A standard ferromagnetic target object in a specific size through the differential sensor along with the direction of sensing can obtain a signal, which is similar to the sine wave. The output signal is linear within a range of 1.5mm near the center position.
Marks:
- Because the sensor is damaged easily, it is forbidden to squeeze, collide and scratch the detection surface;
- The sensor should be fixed reliably and move along the sensing direction in the installation process;
- The sensor working temperature should be -30~70 ℃. Temperature over the range will affect the lifetime;
- The rated working voltage and the maximum working voltage of the differential magnetoresistive sensor is respectively 5V and 10V.
Please read the related post for more information about the magnetoresistance sensor: https://www.powerwaywafer.com/magnetoresistance-sensor.html
For more information, please contact us email at victorchan@powerwaywafer.com and powerwaymaterial@gmail.com.

