PAM-XIAMEN can provide AlGaN/GaN HEMT heterostructure, like GaN on SiC HEMT wafer, for more wafer parameter please read: https://www.powerwaywafer.com/gan-wafer/gan-hemt-epitaxial-wafer.html. Based on the strong polarization-induced effect and the huge energy band shift, the interface of the III-nitride heterostructure can form a strong quantum localized high-concentration two-dimensional electron gas (2DEG) system, becoming the semiconductor material system that can provide the highest concentration of 2DEG so far. The 2DEG electron mobility is an important parameter of AlGaN/GaN heterostructures, and its magnitude directly affects the frequency and power characteristics of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs. The 2DEG has a strong dependence on the Al composition in the heterojunction, the thickness of the potential barrier and the thickness of the GaN channel layer.
1. Influencing Factors of 2DEG Concentration in GaN HEMT Epitaxy
The main factors will affect 2DEG concentration are as follows:
Al composition: the main factor determining the concentration of 2DEG; 2DEG density is increasing with Al composition shown as Fig. 1:
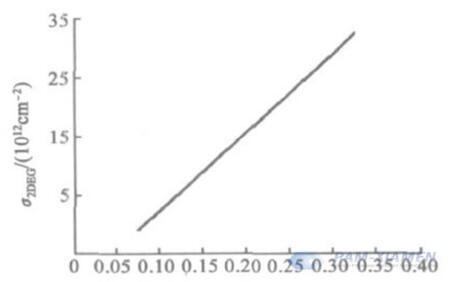
Fig. 1 Relationship between 2DEG Density and Al Composition in AlxGa1-xN Alloys
Thickness of AlGaN barrier layer: an important factor affecting 2DEG, see Fig. 2:
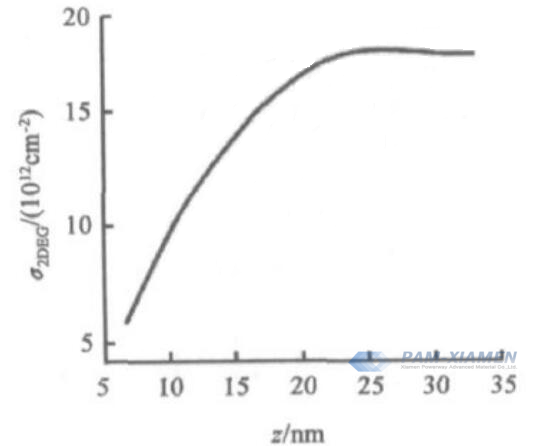
Fig. 2 Relationship between 2DEG and AlGaN Barrier Layer Thickness in AlGaN/GaN Structure
Barrier layer doping: can increase the concentration of 2DEG; the relationship between the peak concentration of 2DEG and the doping concentration in GaN when different barrier layers are doped, shown as Fig. 3:

Fig. 3 Concentration of 2DEG Changes with Doping Concentration of the Barrier Layer
2. Factors Influencing 2DEG Carrier Mobility in GaN HEMT Wafer
The Al composition and barrier thickness of AlGaN/GaN will influence the mobility of GaN HEMT heterostructure, shown in Fig.4 and Fig.5.
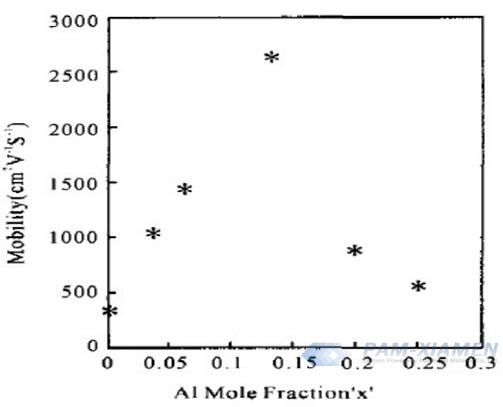
Fig. 4 Al Content Affects AlGaN/GaN HEMT Wafer Mobility
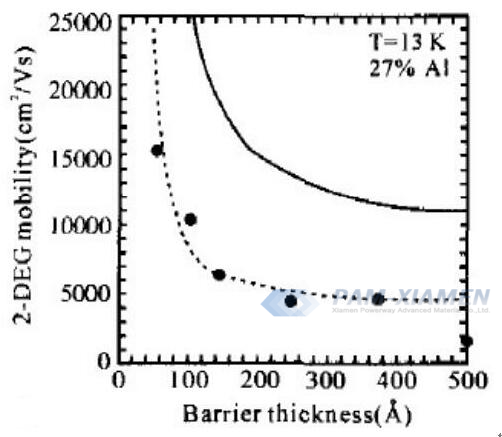
Fig. 5 Variation of Carrier Mobility with Barrier Layer Thickness in AlGaN/GaN HEMT Structure
In addition, the scattering mechanisms will affect carrier mobility in AlGaN/GaN heterostructures mainly include:
Alloy random scattering;
Ionized impurity scattering;
Interface roughness scattering;
Acoustic phonon scattering;
And polarized optical phonon scattering.
The electron mobility of AlGaN/(AlN)/GaN HEMT structure changes with temperature at different scattering mechanisms, details please view Fig. 6:
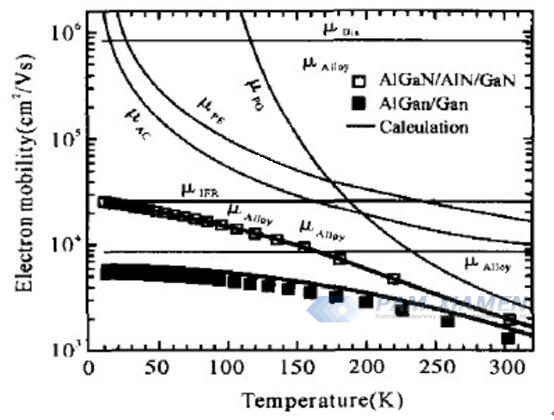
Fig. 6 Various Scattering Mechanisms and Mobility-Temperature Relationships in AlGaN/(AlN)/GaN Heterostructures
The product of the 2DEG concentration and mobility determines the performance of the device, so in order to improve the performance of AlGaN/GaN HEMTs, the product of the 2DEG areal density and mobility must be increased. However, it is unavoidable that increasing the 2DEG concentration often leads to a decrease in carrier mobility. Therefore, it needs to balance the relationship between 2DEG concentration and carrier mobility.
For more information, please contact us email at victorchan@powerwaywafer.com and powerwaymaterial@gmail.com.

