Indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) sensors are supplied by PAM-XIAMEN, a InGaAs sensor manufacturer. Its working principle is actually the principle of shortwave infrared (SWIR). And the working principle of SWIR-based sensor is similar to that of CMOS-based sensor, converting photons into electrons. SWIR technology must use InGaAs, MCT or HgCdTe, which are sensitive to infrared light.
The sensitivity of these sensors to different wavelengths depends on their chemical structure. Both of these materials require strong cooling to achieve the proper signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), but MCT usually requires cryogenic cooling. Therefore, InGaAs sensor is more commonly used because it is more practical and economical. Following is the specific info of the SWIR-based InGaAs sensor.
1. Specifications of InGaAs Sensor
Item 1:
| Item | PAM-SW640-F15c |
| Size | 640 x 512 |
| Pixel Size | 15μm |
| Spectral Response | 0.9 ~ 1.7 μm |
| Effective Area | 9.6mm x 7.68mm |
| Fill Factor | 100% |
| Quantum Efficiency | ≥65 % (1.0 ~ 1.6 um) |
| Detection rate D* | ≥5 x 1012cm Hz1/2W-1 |
| Noisy Electronics | 50 e– @HG |
| Full Well Capacity | 1.8 x 106e–( @LG,1.8V )
7.3 x 104e–( @MG,1.8V ) 1.7 x 104e–( @HG,1.8V ) |
| Dynamic Range | 76 dB (Linear mode)
120 dB (Logarithmic mode) |
| Spectral Response Non-uniformity | <3% |
| Operable Pixel Rate | >99.5% |
| Exposure Time | 37 μs ~ frame time |
| TEC Refrigeration | TEC 1 |
| Read Mode | ITR, IWR, NORO, IMRO |
| Operating Temperature | -40 ~ 60℃ |
| Storage Temperature | -40 ~ 70℃ |
Item 2:
| Item | PAM-SW320-F30a |
| Size | 320 x 256 |
| Pixel Size | 30μm |
| Spectral Response | 0.9 ~ 1.7 μm |
| Effective Area | 9.6 mm x 7.68 mm |
| Fill Factor | >99% |
| Quantum Efficiency | ≥65%(1.0 ~ 1.6 μm) |
| Detection rate D* | ≥5 x 1012cm Hz1/2W-1 |
| Noisy Electronics | 50 e– @HG |
| Full Well Capacity | 3.5 x 106e–( @LG )
1.7 x 104e– ( @HG ) |
| Spectral Response Non-uniformity | ≤4% |
| Operable Pixel Rate | >99% |
| Exposure Time | 1 μs ~ frame time |
| Read Mode | ITR, IWR, IMRO |
| Operating Temperature | -40 ~ 60℃ |
| Storage Temperature | -40 ~ 70℃ |
Item 3:
| Item | PAM-SW1280 |
| Size | 1280 x 1024 |
| Pixel Size | 15 μm |
| Spectral Response | 0.9-1.7μm |
| Quantum Efficiency | >70% (1.0um ~ 1.6um) |
| Noisy Electronics | 40e– @HG |
| Exposure Time | 1 μs ~ frame time |
| Read Mode | ITR, IWR, CDS |
| Operating Temperature | -40 ~ 70℃ |
| Storage Temperature | -40 ~ 70℃ |
Note: TEC refrigeration can be provided on request to improve the sensitivity of the detector. There are 3 main features of PAM-XIAMEN’s InGaAs sensor:
-Low dark current
-High quantum efficiency
-High operability
2. About the Shortwave Infrared InGaAs Sensor
There are three “atmospheric windows” from 1.5µm to 14µm, which are defined as: short wave (SWIR): 1.5 µm – 2.5 µm, medium wave (MWIR): 2 µm-5 µm and long wave (LWIR): 7.5 µm-14 µm. Generally, the wavelength range of short-wave infrared is 0.85-2.5μm, the main sensing material is InGaAs.
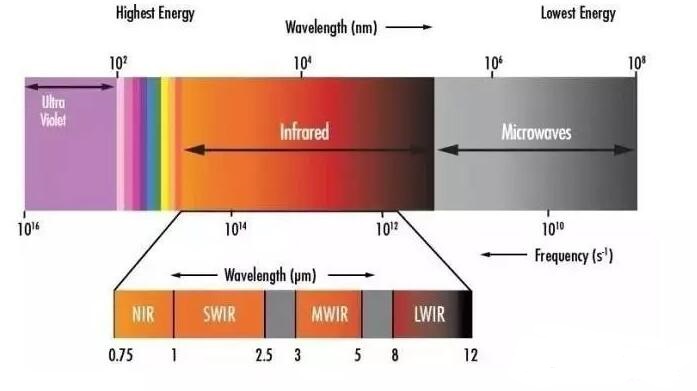
Short-wave Infrared Range
The sensitive of short-wave infrared range has become a reality since the development of InGaAs sensors. But why use shortwave infrared?
2.1 The Usefulness of Indium Gallium Arsenide Image Sensor
First of all, there is a basic fact: light in the short-wave infrared band is invisible to the human eye. The visible light spectrum extends from the wavelength of 0.4 microns (near ultraviolet light, which is blue to the human eye) to 0.7 microns (dark red). Wavelengths longer than the wavelength of visible light can only be seen with dedicated sensors such as InGaAs.
However, although light in the short-wave infrared region is invisible to the human eye, this light can interact with objects in a manner similar to the wavelength of visible light. In other words, short-wave infrared light is reflected light; its reflection from an object is very similar to visible light. Due to this reflective nature, short-wave infrared light will have shadows and contrasts on its images. InGaAs sensor camera images are comparable to visible light images in terms of resolution and detail. However, the colors of short-wave infrared images are not actual colors. This can make the object easy to be identified.
2.2 InGaAs Sensor Advantages
What makes it useful? InGaAs sensor can be made extremely sensitive, it can count individual photons one by one. In this way, when it is made with thousands or millions of tiny point-shaped sensors or sensor pixels, the InGaAs camera can work in very dark conditions.
Take the night vision goggles for example. They work by sensing and amplifying reflected visible starlight or other ambient light. They are often called image intensifier tubes. Therefore, the technology is very suitable for direct observation night vision goggles. But when an image needs to be transmitted to a remote place, there is no practical method that can not be restricted by reliability and sensitivity. Since light can be converted into electrical signals, InGaAs sensors are inherently suitable for standard storage or transmission technologies.
There is another big advantage to using shortwave infrared at night. A camera made of a short-wave infrared InGaAs sensor can help people “see” the target at night without moonlight more clearly.
3. Characteristics of InGaAs Sensor
The shortwave infrared imaging technology based on InGaAs sensor has the characteristics: high sensitivity, high resolution, day and night imaging, concealed lighting, no need for low temperature refrigeration, small size and low power.
4. Applications of SWIR InGaAs Sensor
Due to its outstanding application features such as high recognition, all-weather adaptation, low-light night vision, stealth active imaging, and simple optical configuration, shortwave infrared InGaAs line sensor, InGaAs area sensor or InGaAs image sensor makes it suitable for aerospace remote sensing, archaeological identification, public security, industrial inspection, and medical diagnosis.
Related News of Indium Gallium Arsenide Sensor:
InGaAs EPI on InP( Semi-insulating)
Structure for InGaAs photodetectors
For more information, please contact us email at victorchan@powerwaywafer.com and powerwaymaterial@gmail.com.

